Filter ratings are an often misunderstood area of contamination control. On several recent occasions, I have witnessed someone describing a filter by its nominal rating. A nominal rating is anarbitrary micrometer value given to the filter by the manufacturer. These ratings have little to no value. Tests have shown that particles as large as 200 microns will pass through a nominally rated 10-micron filter. If someone tries to sell you a filter based on an "excellent" nominal rating offive microns, run away.
在雜質(zhì)控制領(lǐng)域�,過(guò)濾器的評級常常會(huì )被用戶(hù)誤解��。*近在一些場(chǎng)合��,我看到有人用名義過(guò)濾等級(國內常稱(chēng)為:名義精度)來(lái)描述過(guò)濾器的性能���。名義過(guò)濾等級事實(shí)上是濾清器制造商賦予濾清器產(chǎn)品的一個(gè)標稱(chēng)值��。這種名義等級基本上沒(méi)有什么意義�。試驗表明�����,即便是尺寸大至200微米的顆粒依舊可以通過(guò)一個(gè)名義過(guò)濾等級為10微米的過(guò)濾器����。如果有人想賣(mài)給一個(gè)“上等的”濾清器給你����,并告訴你這個(gè)產(chǎn)品標稱(chēng)的名義過(guò)濾等級為5微米�����,那么����,你可以閃人了���。
Absolute Rating
**評級
Another common rating for filters is the absolute rating. An absolute rating gives the size of the largest particle that will pass through the filter or screen. Essentially, this is the size of the largest opening in the filter although no standardized test method to determineits value exists. Still, absolute ratings are better for representing the effectiveness of a filter over nominal ratings.
另一個(gè)常見(jiàn)的濾清器評級是所謂的**評級����。**評級給出*大能夠通過(guò)該濾清器的顆粒尺寸�����。從本質(zhì)上講��,并沒(méi)有哪個(gè)標準的檢測方法是通過(guò)評估濾清器*大的通過(guò)尺寸進(jìn)而評判濾清器性能的����。不過(guò)���,**評級在某種程度上來(lái)說(shuō)�,與名義過(guò)濾等級相比����,能更好地描述過(guò)濾器的有效性�����。
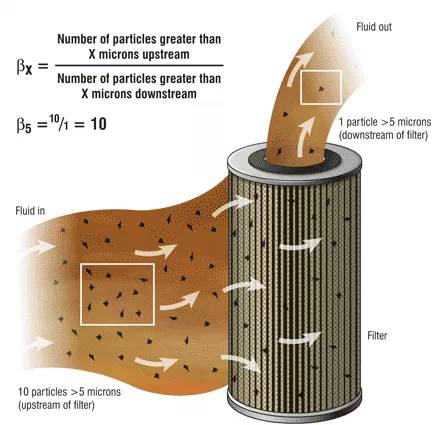
Figure 1(圖1)
Beta Rating
β 比
The best and most commonly used rating in industry is the beta rating. The beta rating comes from the Multipass Methodfor Evaluating Filtration Performance of a Fine Filter Element (ISO16889:1999).
在工業(yè)領(lǐng)域��,*好和*常見(jiàn)的評級是用β比(或稱(chēng)β率)�����。Beta比是來(lái)自:“利用多次通過(guò)法評估精過(guò)濾器過(guò)濾性能” 這個(gè)標準�。(ISO 16889:1999)
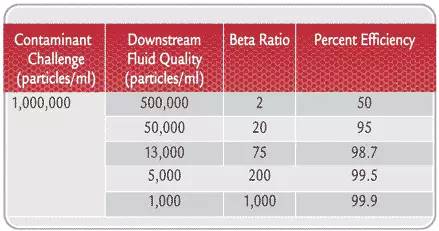
Table 1. Effect of Filtration Ratio (Beta Ratio) on Downstream Fluid Cleanliness
表1. 過(guò)濾率(β比)對下游燃料清潔度的影響
To test a filter, particle counters accurately measure the size and quantity of upstream particles per known volume of fluid, as well as the size and quantity of particles downstream of thefilter. The ratio is defined as the particle count upstream divided by the particlecount downstream at the rated particle size. Using the beta ratio, afive-micron filter with a beta 10 rating, will have on average 10 particles larger than five microns upstream of the filter for every one particle five microns or greater downstream.
測試濾清器的性能�,顆粒計數器可以**地測量濾清器上游已知體積的燃油內還有的顆粒尺寸和數量��,同樣也對下游進(jìn)行測量���。過(guò)濾率的定義是指定尺寸的上游的顆粒物的數量除以下游顆粒物的數量�。使用β比��,一個(gè)5微米β比為10的濾清器�,意味著(zhù)上游平均每10個(gè)大于5微米的顆粒物��,經(jīng)過(guò)此過(guò)濾器過(guò)濾�����,下游還會(huì )有1個(gè)大于5微米的顆粒物���。
The efficiency of the filter can be calculated directly from the beta ratio because the percent capture efficiencyis ((beta-1)/beta) x 100%. A filter with a beta of 10 at five microns is thus said to be 90 percent efficient at removing particles five microns and larger.
濾清器的過(guò)濾效率將可以直接用β比換算:(β-1) / β * 100% = 效率�。即����,如果一個(gè)濾清器對5微米的β比是10����,也就是說(shuō)��,它對于大于等于5微米的顆粒物的過(guò)濾效率是90%�。
Caution must be exercised when using beta ratios to compare filters because they do not take into account actual operating conditions such as flow surges and changes in temperature.
當然���,在利用β比來(lái)對濾清器性能進(jìn)行比較的時(shí)候����,必須要注意是否有考慮到實(shí)際的操作環(huán)境�,比如流量和溫度的變化�����。
A filter's beta ratio also does not give any indication of its dirt-holding capacity, the total amount of contaminant that can be trapped by the filter through out its life, nor does it account for its stability or performance over time.
一個(gè)過(guò)濾器的β比并沒(méi)有指出其容納污染物的能力��,一個(gè)濾清器在其整個(gè)有效壽命期間所能捕獲的雜質(zhì)�����,并沒(méi)有考慮到其穩定性或者性能隨著(zhù)時(shí)間推移而發(fā)生的變化����。
Nevertheless, beta ratios are an effective way of gauging the expected performance of a filter.
不論如何��,β比是一個(gè)有效的測量濾清器預期性能的參數����。
I hope this knowledge of filter efficiency ratings enables you to make a more informed purchase the next time you buy a filter.
希望這個(gè)關(guān)于濾清器效率評級的文章能讓您在下次購買(mǎi)濾清器的時(shí)候更加明智��。